Ac Trade

What is the latest update on the NBA trade deadline ?
The NBA trade deadline has passed, resulting in severalThe NBA trade deadline has passed, resulting in several impact the league's play resulting in several notable trades that could impact the league's playoff race and future team dynamics. Key trades include the Boston Celtics acquiring Evan Fournier, the San Antonio Spurs sending LaMarcus Aldridge to the Brooklyn Nets, the Golden State Warriors acquiring Andrew Wiggins and D'Angelo Russell, and the Miami Heat acquiring Andre Iguodala. These moves have implications for both the teams involved and the league as a whole, with potential shifts in power and long-term effects on player development and team rebuilding efforts. Fan reactions to these trades have been mixed, with excitement and disappointment among different fan bases.

What are some common applications for AC stepping motors ?
AC stepping motors have a wide range of applications due to their precise control and high torque output. Here are some common uses: 1. Printers and Plotters: AC stepping motors are used in printers and plotters to move the print head or pen with precision, and they can control the speed of the print head or pen, allowing for variable printing speeds. 2. CNC Machines: In computer numerical control (CNC) machines, AC stepping motors are used to control the path of the cutting tool and adjust the feed rate of the tool, allowing for precise machining of parts. 3. Robotics: AC stepping motors are often used in robotic joints to provide precise movement and positioning, and they can control the force applied by the robot's end effector, allowing for delicate manipulation of objects. 4. Textile Industry: In textile machinery, AC stepping motors are used to feed fabric through the machine at a controlled rate and control the pattern being woven into the fabric by adjusting the position of the weaving elements. 5. Automation Systems: AC stepping motors are used to control the speed and direction of conveyor belts in automation systems, and they are often used as actuators in automated systems, providing precise control over the position and movement of components.

Can an AC stepping motor be used in robotics applications ?
AC stepping motors can be used in robotics applications, offering precise control and high torque. However, they have speed limitations and can overheat, requiring cooling mechanisms. Consider application requirements and compatibility with control systems before choosing an AC stepping motor for a robotic project.

What is the difference between a bipolar and unipolar AC stepping motor ?
AC stepping motors are widely used in various applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and automation systems. They convert electrical pulses into mechanical movements with high precision and repeatability. There are two main types of AC stepping motors: bipolar and unipolar. This article will discuss the differences between these two types of motors. Bipolar AC stepping motors have two windings that are connected in series or parallel. Each winding is energized by an alternating current (AC) source, which creates a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field depends on the polarity of the current flowing through the windings. By changing the polarity of the current flowing through the windings, the direction of rotation can be reversed. Bipolar AC stepping motors have several advantages over unipolar motors, including higher torque output at lower speeds, better heat dissipation due to larger surface area of the windings, and more efficient use of electrical energy due to lower resistance of the windings. Unipolar AC stepping motors have only one winding that is energized by an alternating current (AC) source. The direction of the magnetic field created by this winding is always the same, regardless of the polarity of the current flowing through it. Unlike bipolar motors, unipolar motors cannot change the direction of rotation without additional hardware. Unipolar AC stepping motors have some advantages over bipolar motors, including simpler control circuitry since only one winding needs to be controlled, lower cost due to fewer components required for operation, and smaller size and weight, making them suitable for compact applications. In conclusion, bipolar and unipolar AC stepping motors differ in terms of their number of windings, ability to reverse direction, torque output, heat dissipation, efficiency, control circuitry complexity, cost, and size/weight. Depending on the specific requirements of your application, you may choose either type of motor based on these factors.

What is an AC stepping motor and how does it work ?
An AC stepping motor is a type of electric motor that operates on alternating current and moves in discrete steps. It is commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, CNC machines, 3D printers, and automation systems. The motor's movement is achieved by energizing its coils in a specific sequence, causing the rotor to turn a fixed angle for each step. The components of an AC stepping motor include the stator, rotor, and drive system. The stator is the stationary part of the motor containing coils or windings. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, which has magnetic teeth. The drive system controls the sequence and timing of electrical pulses sent to the stator coils. The operational principle of an AC stepping motor involves winding energization, rotor alignment, stepping action, and repeating sequence. When an electrical current is applied to the stator windings, it creates a magnetic field. The magnetic field interacts with the rotor's magnetic teeth, causing them to align with the stator's field. By changing the sequence of the energized coils, the rotor is forced to rotate to a new position where the teeth again align with the stator's magnetic field. Continuously changing the energized coils causes the rotor to move in a series of small steps. There are two phases of operation for an AC stepping motor: single phase and multi-phase. Single phase operates using only one phase of AC power, typically for simpler applications. Multi-phase uses multiple phases of AC power for more complex movements and higher torque requirements. Control and drive systems for an AC stepping motor include microstepping, drivers, and controllers. Microstepping allows the motor to move in even smaller steps than its inherent step angle by controlling the current through the windings. The driver translates digital commands into the appropriate current levels and patterns required by the motor. The controller sends commands to the driver based on input from sensors or user interfaces. Advantages of an AC stepping motor include precision, simple control, and high reliability. Disadvantages include low top speed, resonance issues, and torque drop-off. In summary, an AC stepping motor converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements through the interaction of its stator and rotor components. Its operational simplicity and precision make it ideal for various control applications despite some limitations in speed and resonance concerns.

What are the advantages of using an AC stepping motor compared to a DC stepping motor ?
The text discusses the advantages of using AC stepping motors compared to DC stepping motors. The main points include: 1. **Simplified Drive Circuitry**: AC stepping motors have simpler drive circuitry than DC stepping motors, leading to fewer components and a more streamlined design, which reduces complexity and lowers manufacturing costs. 2. **Higher Torque Output**: AC stepping motors typically offer higher torque output than DC stepping motors, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque at low speeds. This also leads to improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption. 3. **Better Heat Dissipation**: AC stepping motors often have better heat dissipation capabilities due to their larger surface area and improved cooling mechanisms, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures without overheating and extending their lifespan. 4. **Compatibility with Standard AC Power Sources**: AC stepping motors are compatible with standard AC power sources widely available in industrial and commercial settings, eliminating the need for additional power supplies or conversion equipment and simplifying installation. 5. **Lower Maintenance Requirements**: AC stepping motors generally require less maintenance than DC stepping motors, as they have fewer moving parts and simpler drive circuitry, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Overall, the text highlights that AC stepping motors offer significant benefits over DC stepping motors in terms of simplicity, performance, efficiency, compatibility, and maintenance, making them a popular choice for various applications where precision control and reliability are essential.

Can I trade in my old iPhone for a new one ?
This article discusses various options for trading in an old iPhone for a new one, including Apple's trade-in program, carrier trade-in programs, and third-party trade-in websites. It highlights the benefits and considerations of each option and provides tips on how to get the most value for your old device.

How have recent trade tensions impacted international finance ?
Recent trade tensions have had a significant impact on international finance, increasing uncertainty, contributing to volatility in financial markets, and leading to changes in investment patterns. Companies may hesitate to make long-term commitments or expand into new markets due to the uncertainty created by trade tensions. Additionally, sudden announcements of new tariffs or trade restrictions can cause stock prices to drop rapidly, while news of a potential resolution can cause them to rise quickly. Changes in investment patterns may also occur as companies invest more heavily in countries where they are less likely to face trade barriers, and investors shift their portfolios away from industries that are likely to be impacted by trade tensions.

How do international trade agreements influence environmental policies and sustainability efforts ?
International trade agreements significantly influence environmental policies and sustainability efforts through harmonization of standards, potential for environmental dumping, promotion of green trade practices, and challenges in balancing trade liberalization with environmental protection. These agreements can either elevate global environmental standards or lead to a race to the bottom in regulatory protections. Policymakers must navigate the complexities of these agreements to ensure they support sustainable development goals without undermining environmental commitments.

How do ecological taxes compare to other environmental policies, such as cap-and-trade systems ?
The text discusses the comparison of two environmental policies: ecological taxes and cap-and-trade systems. It explains what these policies are, their advantages, disadvantages, and concludes that the choice between them depends on political feasibility, administrative capacity, and public acceptance.

How do climate change negotiations affect global trade and economic systems ?
Climate change negotiations play a crucial role in shaping global trade and economic systems. These negotiations aim to find solutions to the challenges posed by climate change, such as reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting renewable energy sources, and protecting biodiversity. The outcomes of these negotiations have far-reaching implications for international trade, investment, and economic development. In this article, we will explore how climate change negotiations affect global trade and economic systems. One of the key impacts of climate change negotiations on international trade is the imposition of tariffs and subsidies on goods and services that contribute to climate change. For example, countries may impose higher tariffs on imported goods that are produced using high levels of carbon emissions or other environmentally harmful practices. Similarly, governments may provide subsidies to domestic industries that adopt sustainable practices or invest in renewable energy technologies. These measures can create trade barriers and distort market competition, affecting global trade patterns. Another way in which climate change negotiations can influence international trade is through the implementation of carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems. These mechanisms aim to internalize the external costs of carbon emissions by making polluters pay for their emissions. As a result, companies that rely heavily on fossil fuels or produce high levels of emissions may face increased costs, making their products less competitive in global markets. On the other hand, companies that invest in low-carbon technologies or adopt sustainable practices may gain a competitive advantage. Climate change negotiations often lead to the adoption of stricter environmental standards and regulations at both national and international levels. These standards can affect international trade by creating compliance costs for exporters and importers. For instance, companies that export goods to countries with stringent environmental regulations may need to invest in cleaner production processes or face penalties for non-compliance. Similarly, importers may prefer to source goods from suppliers that meet certain environmental standards, affecting trade flows and market access. Climate change negotiations also have significant implications for investment and economic development. As countries commit to achieving ambitious climate targets, there is an increasing demand for green finance and investment in sustainable projects. This can create new opportunities for investors and businesses that focus on renewable energy, energy efficiency, and other low-carbon sectors. However, it can also lead to capital flight from traditional fossil fuel industries, affecting economies that rely heavily on these sectors. Climate change negotiations often include provisions for technology transfer and innovation cooperation between developed and developing countries. This can help bridge the gap between countries with different levels of technological capabilities and promote sustainable development worldwide. By facilitating the transfer of clean energy technologies and supporting research and development efforts, climate change negotiations can foster economic growth and job creation in emerging markets. Finally, climate change negotiations address the urgent need for adaptation financing and support for vulnerable communities affected by climate change. This includes funding for infrastructure improvements, disaster risk reduction, and other measures that help countries adapt to changing climate conditions. While these efforts are essential for protecting human lives and livelihoods, they also represent significant economic opportunities for businesses involved in climate resilience and adaptation services. In conclusion, climate change negotiations have far-reaching implications for global trade and economic systems. By imposing tariffs and subsidies, implementing carbon pricing mechanisms, setting environmental standards, promoting green finance and investment, facilitating technology transfer and innovation, and providing adaptation financing and support, these negotiations shape the future direction of international trade and economic development. As we continue to grapple with the challenges posed by climate change, it is crucial for policymakers, businesses, and civil society to work together to ensure that our responses to this global challenge are aligned with our collective goals for sustainable prosperity.

How does a carbon tax compare to other climate policies, such as cap-and-trade ?
**Comparison between Carbon Tax and Cap-and-Trade Climate Policies:** **Effectiveness:** - **Carbon Tax**: Depends on tax rate, revenue recycling, and international cooperation. Higher rates may reduce emissions but impact the economy negatively. - **Cap-and-Trade**: Depends on the stringency of the cap, market mechanisms, and offsetting mechanisms. A strict cap can lead to significant emissions reductions. **Economic Implications:** - **Carbon Tax**: Incentivizes innovation, impacts consumers (especially low-income households), and can stimulate economic growth through green technologies. - **Cap-and-Trade**: Introduces cost uncertainty, risks market manipulation, and can create jobs in new technologies and industries related to emissions reductions. **Implementation Challenges:** - **Carbon Tax**: Faces political opposition, equity concerns, and requires international coordination for maximum effectiveness. - **Cap-and-Trade**: Requires complex setup and management, strict enforcement, and may face public opposition if perceived as legitimizing pollution. **Conclusion:** Both policies have pros and cons in addressing climate change. The choice often depends on political feasibility, economic considerations, and public acceptance. What's crucial is taking effective action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

Can you explain the differences between AC and DC drive motors ?
Electric motors are essential components in various industries, ranging from manufacturing to transportation. Two of the most common types of electric motors are AC (Alternating Current) and DC (Direct Current) drive motors. While both serve similar functions, there are several differences between them that affect their performance and applications. AC and DC drive motors differ in their construction and design, with AC motors having a simpler design with fewer parts, while DC motors have more complex designs with additional components such as brushes and commutators. This complexity can lead to higher maintenance costs for DC motors compared to AC motors. One of the main differences between AC and DC drive motors is their ability to control speed. AC motors generally operate at a fixed speed, which makes them less suitable for applications requiring variable speed control. On the other hand, DC motors offer precise speed control, making them ideal for applications such as robotics, CNC machines, and conveyor systems. AC motors are generally more efficient than DC motors due to their simpler design and lower power consumption. However, the efficiency of a motor also depends on its size, load capacity, and operating conditions. In some cases, DC motors may be more energy-efficient when used in low-power applications or when precise speed control is required. Another difference between AC and DC drive motors is their starting torque. AC motors generally have a higher starting torque than DC motors, which makes them better suited for heavy-duty applications such as pumps, fans, and compressors. DC motors, on the other hand, provide a smoother start-up but may require additional components to achieve the desired starting torque. The cost and availability of AC and DC drive motors vary depending on their size, type, and manufacturer. Generally, AC motors are more widely available and less expensive than DC motors due to their simpler design and lower production costs. However, the total cost of ownership should also consider factors such as maintenance, repair, and energy consumption over the motor's lifetime.

How do you control the speed and torque of an AC stepping motor ?
The text provides a comprehensive overview of controlling the speed and torque of an AC stepping motor, emphasizing the importance of understanding its basic principles and utilizing appropriate control techniques. Key points include the motor's working principle, torque generation, and step resolution, as well as various control methods such as pulse rate modulation, microstepping, closed-loop control, current limiting, voltage control, and soft start/stop. Practical considerations like drive system compatibility, thermal management, load factors, and safety precautions are also highlighted for optimal motor performance and longevity.
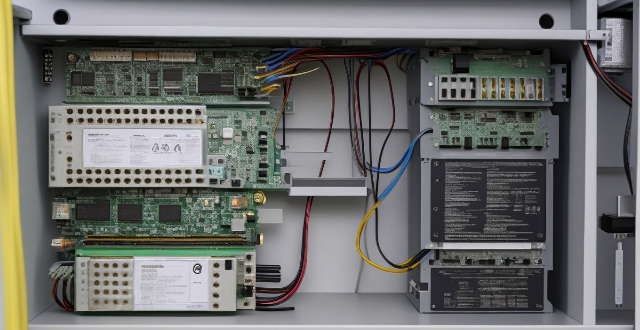
How do you connect an AC stepping motor to a microcontroller or driver board ?
Connecting an AC stepping motor to a microcontroller or driver board involves selecting the right board, connecting the power supply, attaching the motor, programming the board, testing the connection, and troubleshooting any issues. Materials needed include the motor, board, power supply, wires, and optionally a breadboard for temporary connections. Tips include double-checking connections and code, using a breadboard before soldering, and following safety guidelines when working with high voltages.

How do you choose the right AC stepping motor for your project ?
Choosing the right AC stepping motor requires understanding project needs, selecting the appropriate motor type, ensuring compatibility with control systems, considering physical constraints, evaluating performance characteristics, accounting for environmental factors, managing budgetary considerations, relying on supplier support and reputation, and conducting thorough testing.

What are the key parameters to consider when selecting an AC stepping motor ?
Selecting an AC stepping motor involves considering key parameters such as torque, step angle, voltage and current ratings, resolution, size and weight, compatibility with the control system, and cost. These factors ensure the motor meets the application's requirements, providing enough rotational force, handling load demands, fitting within space and weight restrictions, and operating smoothly and precisely. Compatibility with the controller is crucial for proper operation, while cost considerations help stay within budget constraints.

How do you troubleshoot common issues with AC stepping motors, such as missing steps or low torque ?
Troubleshooting common issues with AC stepping motors involves addressing problems such as missing steps or low torque. This is done by checking the power supply, examining the drive system, analyzing mechanical components, evaluating control signals, and considering environmental factors. It is important to approach the problem methodically, starting with basic checks before moving on to more complex diagnostics.

How does Cross-Border Payment impact global trade ?
Cross-border payment plays a crucial role in the global trade ecosystem by enabling businesses to buy and sell goods and services internationally. It reduces transaction costs, enhances transparency and efficiency, and promotes economic growth. However, challenges related to regulatory compliance, currency fluctuations, and technological barriers need to be addressed.

How can international trade contribute to economic recovery ?
International trade can contribute to economic recovery by providing increased market access, access to cheaper imports, stimulating innovation and competition, and enhancing global integration.

What is the relationship between international trade and climate agreements ?
International trade and climate agreements are interconnected phenomena that impact the global economy and environment. The relationship is complex, involving governments, international organizations, businesses, and civil society. International trade drives economic growth but also leads to increased greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon leakage occurs when industries relocate to countries with weaker environmental regulations. Global value chains contribute to emissions through transportation and production processes. Climate agreements aim to reduce emissions and promote sustainable development by setting targets for countries to achieve through various measures. They also address carbon leakage by including provisions for cooperation and coordination among countries. The relationship between international trade and climate agreements has important implications for sustainable development, including ensuring equitable economic growth, promoting fair competition, supporting innovation in clean technologies, and encouraging collaboration among countries.

How can developing countries benefit from international cooperation ?
Developing countries can benefit from international cooperation in multiple ways, including access to technology and innovation, economic growth and trade opportunities, improved healthcare and education, environmental sustainability, and political stability and peace. Technology transfer, research collaborations, capacity building, trade agreements, foreign direct investment, infrastructure development, medical aid, educational exchange programs, renewable energy projects, conservation efforts, clean technology transfer, conflict resolution, democratic institution building, and legal and judicial reform are some of the key areas where developing countries can gain from working with their international counterparts.

How has the issue of climate change impacted international trade and commerce ?
Climate change has significant impacts on international trade and commerce, including disruptions to supply chains due to extreme weather events, changes in agricultural production affecting food security and prices, infrastructure damage leading to increased costs for businesses, rising energy costs as countries transition to renewable sources, carbon emissions regulations requiring companies to invest in new technologies, and changing consumer behavior demanding sustainable products. Businesses must adapt to these changes to remain competitive and ensure long-term sustainability.

What are the economic implications of the decisions made at climate summits ?
Climate summits like the UNFCCC COP have far-reaching economic implications, affecting sectors from energy to infrastructure and trade. Decisions made at these events can influence investment patterns, job creation, and national economies. Key impacts include shifts towards renewable energy, green innovation, changes in infrastructure, adjustments in fiscal policies, alterations in international trade dynamics, effects on natural resource management, and increased regulatory compliance costs. These decisions are crucial as they help shape a sustainable and climate-resilient global economy.

How do extreme weather events due to climate change impact international trade and logistics ?
Extreme weather events, often exacerbated by climate change, have a profound impact on international trade and logistics. These events can disrupt supply chains, increase transportation costs, and lead to shortages of goods and services. The various ways in which extreme weather events affect international trade and logistics include disruption of supply chains through transportation disruptions and production disruptions, increased transportation costs due to higher fuel prices and insurance costs, and shortages of goods and services due to reduced availability and price volatility. To mitigate these impacts, it is essential for governments, businesses, and individuals to take action to address climate change and adapt to its effects on international trade and logistics.

Can you provide examples of successful international cooperation initiatives ?
Successful International Cooperation Initiatives International cooperation is a vital aspect of global progress, enabling countries to work together towards common goals. Here are some examples of successful international cooperation initiatives: 1\. The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) aims to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that prevents dangerous human interference with the climate system. It has been ratified by 197 parties, making it one of the most widely accepted international agreements. 2\. The World Health Organization (WHO) is the directing and coordinating authority on health within the United Nations system. It provides leadership, research, norms and standards, and technical support to countries worldwide. 3\. The International Space Station (ISS) is a joint project among five space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (European Space Agency), and CSA (Canadian Space Agency). It serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory. 4\. The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) is an international agreement between governments aimed at ensuring that international trade in wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival. It regulates or bans trade in species listed in its appendices.

How has Indian cuisine evolved over time ?
The evolution of Indian cuisine is a result of various factors such as geography, climate, history, culture, and trade. India's diverse geography and climate have led to unique culinary traditions in each region, with coastal areas known for seafood dishes and northern plains famous for dairy products and bread. Historical influences like the Mughal era and British colonial period have also shaped Indian cuisine, introducing fusion dishes and bakeries. Trade routes and globalization have integrated foreign flavors into Indian dishes, while regional variations highlight the country's culinary diversity. Modern innovations include fusion dishes and healthier versions of traditional recipes. Overall, Indian cuisine reflects the nation's rich cultural diversity and adaptability to changing trends.

What is the role of international cooperation in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals ?
The text discusses the crucial role of international cooperation in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), which aim to address global challenges such as poverty, inequality, climate change, and environmental degradation. The SDGs cannot be achieved by individual countries alone but require collective action and collaboration at the global level. Key points include the need for global solutions to interconnected issues like climate change; sharing knowledge and best practices between countries; mobilizing financial resources and expertise; promoting policy coherence across sectors; and strengthening multilateral institutions like the United Nations. Examples of international cooperation in achieving the SDGs include climate change agreements like the Paris Agreement, global health initiatives against diseases like HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, and trade agreements that can promote sustainable development if designed correctly. Overall, international cooperation is an integral part of achieving the Sustainable Development Goals.

In what ways do economic factors influence the development and assessment of climate policies ?
Economic factors play a crucial role in the development and evaluation of climate policies, affecting decision-making processes, implementation measures, and assessments of effectiveness. These influences include cost-benefit analysis considering both direct and indirect costs, as well as quantifying avoided costs and non-market benefits. Economic growth and development must balance immediate needs against long-term sustainability goals, potentially leading to tension between current jobs and investment in cleaner technologies. International trade and competitiveness are impacted by concerns over carbon leakage and green trade barriers. Public acceptance and political will are influenced by perceptions of fairness and economic impacts on different income groups, while innovation and technology development depend on investments in research and development and the affordability of technology transfer. Overall, achieving effective climate action requires a careful consideration of economic dynamics alongside environmental objectives.

What are the long-term implications of climate change for global food trade and market stability ?
Climate change is expected to impact global food production, trade, and market stability significantly. Reduced crop yields, unpredictable harvests, decreased livestock productivity, increased disease prevalence, shifting production zones, and increased competition for resources are some of the long-term implications. These changes can lead to price volatility, increased vulnerability to food insecurity, and economic challenges for farmers and consumers. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative effort from governments, international organizations, and stakeholders across the food system to develop strategies that promote resilience and adaptive capacity in the face of climate change.