Advantage Energy

What are the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy ?
The given text is about the advantages and disadvantages of wind energy. The advantages include being renewable and sustainable, environmentally friendly, cost-effective, job creation, and energy independence. On the other hand, the disadvantages are its intermittent nature, land use concerns, noise and visual impact, wildlife impact, and high initial cost.

How does ecological design impact energy efficiency in buildings ?
Ecological design significantly impacts energy efficiency in buildings through various strategies like passive solar design, advanced insulation, renewable energy sources, energy-efficient appliances, water conservation, and sustainable material choices. These practices reduce energy consumption, lower operational costs, and minimize environmental harm.

What is offshore wind energy and how does it work ?
Offshore wind energy is a renewable source that generates electricity from wind turbines installed in bodies of water. It offers advantages such as higher wind speeds and less impact on terrestrial environments but faces challenges including high installation costs and environmental considerations. The process involves converting wind power into electrical energy, which is then transmitted to the mainland grid.
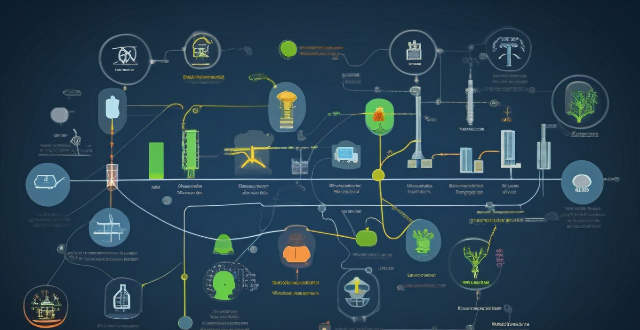
What are the most effective methods for improving industrial energy efficiency ?
The most effective methods for improving industrial energy efficiency include process optimization, using energy-efficient equipment, harnessing renewable energy sources, thermal management, power management, employee training and awareness, employing energy information systems, and complying with policy and regulatory standards. These methods can reduce operational costs, conserve resources, and minimize environmental impact.

What are the benefits of shopping during the discount season ?
Shopping during the discount season offers numerous benefits for consumers, including saving money, getting more value for your money, trying new products, clearing out inventory, avoiding crowds, and taking advantage of promotions. By taking advantage of these opportunities, you can maximize your savings and enjoy a more enjoyable shopping experience.

What are the economic benefits of investing in energy-efficient industrial equipment ?
Investing in energy-efficient industrial equipment can lead to reduced energy costs, increased production efficiency, potential tax incentives and grants, enhanced competitiveness, improved environmental sustainability, and greater long-term asset value. These benefits make such investments financially prudent and strategically sound for businesses looking to remain competitive and responsible in today's market.

What are the most common types of renewable energy sources ?
Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and provide a sustainable way to generate power without depleting the Earth's natural resources or contributing to climate change. Solar energy is harnessed through photovoltaic systems, solar water heaters, and concentrating solar power. Wind energy is captured by onshore and offshore wind turbines. Hydropower is generated through dam-based and run-of-river systems. Geothermal energy is tapped into via dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle power plants. Bioenergy includes biomass combustion, anaerobic digestion, and biofuels. These sources offer clean alternatives to fossil fuels and play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

How do building energy efficiency standards affect the construction industry ?
Building energy efficiency standards have a significant impact on the construction industry by affecting cost implications, design philosophy, regulatory compliance, and market trends. These standards require higher initial costs due to advanced technologies and materials but offer long-term benefits like reduced energy consumption and maintenance costs. They also shift the focus of design towards energy performance and sustainability, leading to integrated design processes and innovative solutions. Compliance with these standards is crucial to avoid penalties and legal issues, while certifications like LEED or WELL can provide a competitive advantage. Finally, building energy efficiency standards influence market trends by driving demand for sustainable construction methods and educating clients about their benefits.

Can permanent magnet motors be used in renewable energy systems such as wind turbines ?
Permanent magnet motors are used in renewable energy systems, including wind turbines, due to their high efficiency and reliability. They offer advantages such as high efficiency, low maintenance, good torque characteristics, size and weight benefits, and adaptability. However, challenges and considerations include cost, thermal management, and dependence on rare earth metals. Overall, permanent magnet motors are a popular choice for efficient and reliable energy conversion in wind power applications.

Is it worth taking advantage of a buy one get one free deal ?
Buy one get one free (BOGO) deals are a popular marketing strategy used by retailers to attract customers and increase sales. The pros of BOGO deals include saving money, trying new products, and stocking up on essentials. However, the cons include impulse buying, limited choices, and potential quality concerns. It is important to carefully consider the pros and cons before deciding whether to take advantage of a BOGO deal.

How can developing countries benefit from implementing renewable energy solutions ?
Renewable energy solutions offer significant benefits for developing countries, including reduced energy costs, job creation, improved health and environmental quality, increased energy security, and climate change mitigation. By investing in renewable energy infrastructure, these countries can build more sustainable and prosperous futures for themselves and their citizens.

What are the alternatives to fossil fuels for energy production ?
The article discusses various alternatives to fossil fuels for energy production, including solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, biomass energy, and nuclear energy. It explains the working principles of each alternative and their advantages and disadvantages. The main advantage of these alternatives is that they produce clean energy with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, reducing the impact on the environment and climate change. However, some of them require significant investment and infrastructure development, while others have safety concerns or limited availability. Overall, the article highlights the potential of these alternatives in providing sustainable and reliable sources of energy for the future.

What are some innovative methods for improving industrial energy efficiency ?
Innovative Methods for Improving Industrial Energy Efficiency - Advanced Technologies: AI and Machine Learning for predictive maintenance and optimization of energy consumption, IoT sensor networks and remote control systems. - Process Optimization Techniques: Heat Recovery Systems like energy recuperation and Combined Heat and Power (CHP), process integration through industrial symbiosis and lean manufacturing. - Building Design and Management: Green architecture using eco-friendly materials and natural lighting/ventilation, Smart Building Management Systems with automated controls and energy management software. - Employee Training and Involvement: Educational programs on energy conservation, skill development for new technologies, participation incentives through reward systems and team challenges.

How efficient is wind energy compared to other renewable sources ?
The efficiency of wind energy is influenced by factors such as capacity factor, technological advancements, and site specificity. Compared to other renewable sources like solar, hydropower, geothermal, biomass, and tidal/wave energy, wind energy has a relatively high capacity factor ranging from 35% to 45%. Technological improvements have increased the efficiency of wind turbines over the years, making them more productive. However, the efficiency of wind farms is highly dependent on the location, with optimal sites achieving higher efficiency rates. In conclusion, wind energy compares favorably to other renewable sources in terms of efficiency, but the choice between different renewable energies often depends on local conditions, economic factors, and technological advancements.

What are the main advantages of permanent magnet motors over other types of electric motors ?
Permanent magnet motors (PMMs) have several advantages over other types of electric motors, including high efficiency, low maintenance requirements, high torque density, wide speed range, and quiet operation. These advantages make PMMs ideal for a variety of applications, from small appliances to industrial machinery.

How can architects and designers incorporate building energy efficiency standards into their work ?
Incorporating Building Energy Efficiency Standards into Architectural and Design Work: - Understanding Energy Efficiency Standards: Research current standards, analyze local climate data. - Design Strategies for Energy Efficiency: Orientation and site layout, insulation and envelope performance, HVAC, lighting and electrical systems, water efficiency. - Material Selection: Sustainable materials, recycled content. - Technology Integration: Building automation systems, solar technology. - Collaboration and Communication: Team collaboration, client education. - Post-Occupancy Evaluation: Monitor performance, feedback loop.

What is wind energy and how effective is it compared to other renewable sources ?
This article provides an overview of wind energy, discussing its definition, effectiveness compared to other renewable sources, cost-effectiveness, environmental impact, scalability, and availability. It highlights the benefits of wind energy as a clean and sustainable source of electricity that can be produced at any scale and in many parts of the world.

Are there any government incentives for installing energy-efficient lighting systems ?
Governments worldwide are offering incentives to encourage the installation of energy-efficient lighting systems. These incentives include tax credits, rebates, grants, and subsidies aimed at reducing energy consumption, lowering greenhouse gas emissions, and promoting sustainable development. Types of government incentives for energy-efficient lighting systems include: 1. Tax Credits: Allow businesses and individuals to deduct a portion of the cost of installing energy-efficient lighting from their taxable income. 2. Rebates: Provide a direct payment to businesses or individuals who install energy-efficient lighting systems. 3. Grants: Financial awards given to support the installation of energy-efficient lighting systems without requiring any initial investment from the recipient. 4. Subsidies: Financial assistance provided by governments to make energy-efficient lighting systems more affordable through mechanisms like low-interest loans and interest rate subsidies. Benefits of energy-efficient lighting systems include significant energy savings, reduced environmental impact, and long-term cost savings. Despite the higher initial cost compared to traditional lighting systems, the reduced energy consumption and maintenance costs can offset the investment over time, making these systems a wise financial decision.

How does clean energy investment compare to traditional energy investment ?
Investing in energy sources is crucial for the development and growth of any economy. However, the choice between clean energy investment and traditional energy investment has become a significant topic of discussion in recent years. This comparison will explore the differences between these two types of investments, focusing on their costs, benefits, and potential impacts on the environment and society.

What are the key factors to consider when planning an energy-efficient building project ?
The text provides a summary of key factors that should be considered when planning an energy-efficient building project. These factors include site selection and orientation, building design and construction, and energy sources and consumption. The location and orientation of the building on the site can have a significant impact on its energy efficiency, as well as the design and construction of the building itself. Consideration should also be given to the sources of energy used by the building and how that energy is consumed. By considering these key factors during the planning stages of an energy-efficient building project, it is possible to create a building that is comfortable, functional, environmentally responsible, and economically sustainable over its lifetime.

How do renewable energy sources contribute to industrial energy efficiency improvements ?
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, and geothermal power play a crucial role in enhancing industrial energy efficiency. They offer benefits such as reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower operating costs, and increased reliability. By adopting these technologies, businesses can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, increase energy independence, and contribute to a more sustainable future.

How is solid-state battery technology improving energy storage ?
Solid-state battery technology is a significant advancement in energy storage, offering advantages such as increased energy density, faster charging times, improved safety, and longer lifespans compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. This technology employs a solid electrolyte material, allowing for a higher concentration of anode and cathode materials within the cell, resulting in more energy stored per unit volume. Solid-state batteries can provide longer runtimes for electronic devices and electric vehicles without increasing their size or weight. The solid electrolyte used in these batteries has higher ionic conductivity than liquid electrolytes, enabling faster movement of lithium ions between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging cycles. This means that devices powered by solid-state batteries can be recharged in significantly less time than those using traditional lithium-ion batteries. Safety concerns have long been associated with lithium-ion batteries due to the risk of thermal runaway, which can lead to fires or explosions. Solid-state batteries address this issue by eliminating the flammable liquid electrolyte found in conventional batteries. Instead, they use a non-flammable solid electrolyte material that does not pose a risk of leakage or combustion. Additionally, the absence of liquid components reduces the likelihood of short circuits occurring within the battery cell, further enhancing overall safety. Solid-state batteries also boast a longer lifespan compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The solid electrolyte used in these batteries is less susceptible to degradation over time, meaning that they can withstand more charging and discharging cycles without losing capacity. This extended lifespan makes solid-state batteries an ideal choice for applications requiring long-term energy storage solutions, such as grid storage systems and renewable energy projects. The benefits offered by solid-state battery technology make it well-suited for a wide range of applications beyond just consumer electronics and electric vehicles. Some potential uses include grid storage systems, renewable energy projects, aerospace & defense, and powering satellites, drones, and other advanced military equipment.

Is geothermal energy a practical solution for colder climates ?
Geothermal energy is a renewable source of energy that comes from the heat generated by the Earth's core. It has been used for centuries in various forms, such as hot springs and geysers. In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in using geothermal energy as an alternative to fossil fuels. But is it a practical solution for colder climates? Let's explore this question further. Advantages of Geothermal Energy in Colder Climates: 1. Reliable Source of Energy: Unlike other renewable sources like solar or wind power, which are dependent on weather conditions, geothermal energy can be harnessed all year round, regardless of the temperature outside. This makes it an ideal source of energy for colder climates where there may be long periods of ice and snow. 2. Low Emissions: Compared to fossil fuels, geothermal power plants produce significantly fewer greenhouse gases and air pollutants. This makes it an environmentally friendly option for communities looking to reduce their carbon footprint. 3. Cost-Effectiveness: While the initial cost of setting up a geothermal power plant can be high, the long-term costs are relatively low compared to other sources of energy. Once established, geothermal power plants require little maintenance and have a lifespan of several decades. This makes it a cost-effective solution for colder climates where energy demands are high due to heating needs. Challenges of Geothermal Energy in Colder Climates: 1. Limited Availability: One of the main challenges of using geothermal energy in colder climates is its limited availability. Not all areas have access to geothermal resources, and even those that do may not have enough heat to generate significant amounts of energy. This means that while geothermal energy can be a practical solution for some areas, it may not be feasible for others. 2. High Initial Costs: As mentioned earlier, the initial cost of setting up a geothermal power plant can be high. This can be a barrier for communities with limited financial resources or those without access to government subsidies or grants. Additionally, drilling equipment and expertise may need to be imported from other countries, adding to the overall cost. 3. Environmental Impact: While geothermal energy is generally considered to be environmentally friendly, there are still some potential impacts associated with its use. For example, drilling activities can disturb wildlife habitats and disrupt local ecosystems. Additionally, if not managed properly, geothermal power plants can release harmful chemicals into the atmosphere or nearby water sources. Conclusion: In conclusion, geothermal energy can be a practical solution for colder climates under certain conditions. Its reliability, low emissions, and cost-effectiveness make it an attractive option for communities looking to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. However, its limited availability, high initial costs, and potential environmental impacts must also be considered before making any decisions about implementing geothermal energy projects in colder climates.

What are the most promising renewable energy technologies for reducing carbon emissions ?
Renewable energy technologies are crucial for reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. They harness natural resources such as wind, solar, hydro, geothermal, and biomass to produce electricity or heat without emitting greenhouse gases. This article discusses the most promising renewable energy technologies for reducing carbon emissions. Solar energy can be generated through photovoltaics (PV) or concentrated solar power (CSP). Wind energy is growing rapidly due to its low cost and minimal environmental impact. Hydropower is a significant source of clean power but has environmental concerns. Geothermal energy has a high capacity factor but limited availability. Bioenergy helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels but requires careful consideration of land use changes. Wave and tidal energy have immense potential but are still in early development stages. Overall, these technologies offer unique benefits and challenges for creating a sustainable future.

How do energy-efficient buildings contribute to reducing carbon emissions in the construction sector ?
Energy-efficient buildings are crucial in the construction sector for reducing carbon emissions, which contribute significantly to global warming and climate change. The importance of urgent action is emphasized by the IPCC's warning about the limited timeframe to limit global warming to 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. Energy-efficient buildings can reduce energy consumption, lower energy bills, improve comfort and health, and contribute to long-term sustainability. Strategies for achieving energy efficiency include passive design strategies, high-performance building envelopes, advanced HVAC systems, retrofitting existing buildings with energy audits and renewable energy sources. Collective action from various stakeholders is necessary to make significant progress towards a sustainable future.

What government incentives are available for individuals or businesses looking to invest in renewable energy technologies ?
Governments worldwide offer incentives for renewable energy investments, including tax credits, grants, feed-in tariffs, net metering, and green bonds, to promote clean energy adoption and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.

How do I use cashback rewards and credit card points to my advantage when shopping ?
Using cashback rewards and credit card points can save money and get more value for purchases. To maximize benefits, choose a suitable credit card, understand the rewards program, make smart spending decisions, redeem rewards wisely, and combine them with discounts and sales.
What is the future of nuclear energy in the energy market ?
The future of nuclear energy is promising, as it has advantages such as low carbon emissions, high energy density and baseload power. However, challenges like safety concerns, waste disposal, and high costs must be addressed. Increasing demand for clean energy, advances in technology, and integration with renewable sources can drive the growth of nuclear energy in the future.

What is energy transition and why is it important ?
Text: Energy transition is the shift from traditional to renewable energy sources, important for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, promoting sustainable development, and improving energy security. Benefits include economic growth, environmental protection, and social progress.

What is the future outlook for clean energy investment ?
The future outlook for clean energy investment is positive, driven by government policies, technological advancements, and growing demand for sustainable energy sources. However, challenges related to intermittency, infrastructure integration, and competition from fossil fuels need to be addressed to ensure the continued growth of the sector.