Pollution Gasoline

Do hybrid cars produce less pollution than traditional gasoline cars ?
Hybrid cars generally produce less pollution than traditional gasoline cars, but the comparison is not straightforward and various factors must be taken into account.

Are gasoline hybrid cars better for the environment than traditional gasoline cars ?
Gasoline hybrid cars, also known as hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), are becoming increasingly popular due to their potential environmental benefits. These vehicles produce fewer emissions compared to traditional gasoline cars and have better fuel efficiency. They also use regenerative braking technology, which captures energy normally lost during braking and stores it in the battery, further improving fuel efficiency and reducing emissions. However, gasoline hybrid cars also have drawbacks such as higher upfront cost, limited electric-only range, and potential environmental impacts from battery production and disposal. Traditional gasoline cars, on the other hand, are generally less expensive than gasoline hybrid cars and have a widespread refueling infrastructure. They are also often simpler and more reliable than gasoline hybrid cars. In conclusion, gasoline hybrid cars offer several environmental benefits over traditional gasoline cars, but they also come with drawbacks. The decision between a gasoline hybrid car and a traditional gasoline car depends on individual preferences, priorities, and circumstances.

Can I still use gasoline in a gasoline hybrid car ?
Gasoline hybrid cars combine a traditional gasoline engine with an electric motor for improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. While they still require gasoline to operate the internal combustion engine, they offer significant savings in fuel costs over time. To maximize fuel efficiency in a gasoline hybrid car, drivers should practice eco-driving techniques, perform regular maintenance, and utilize regenerative braking settings. Gasoline hybrid cars represent a step towards reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and transitioning to cleaner energy sources.

How much more expensive is a gasoline hybrid car compared to a regular gasoline car ?
The cost difference between a gasoline hybrid car and a regular gasoline car can vary depending on several factors such as brand, model, features, and location. However, in general, gasoline hybrid cars tend to be more expensive than regular gasoline cars. Here are some key points to consider: - Gasoline Hybrid Cars: These vehicles typically have a higher initial cost compared to regular gasoline cars due to the additional technology required for the hybrid system. The price difference can range from a few thousand dollars to over $10,000, depending on the make and model. One of the main advantages of gasoline hybrid cars is their improved fuel efficiency. They use both gasoline and electricity to power the engine, which results in better mileage and lower fuel costs over time. While gasoline hybrid cars may have higher repair costs due to their complex systems, they often require less maintenance overall because the electric motor helps reduce wear and tear on the engine. As awareness of environmental issues grows, so does the demand for eco-friendly vehicles like gasoline hybrid cars. This increased demand can help maintain or even increase their resale value over time. - Regular Gasoline Cars: These vehicles are generally less expensive upfront as they do not require the same advanced technology as hybrid cars. These vehicles rely solely on gasoline for power, which can lead to higher fuel consumption and expenses, especially if you drive long distances or frequently idle in traffic. These vehicles may have lower repair costs initially but may require more frequent maintenance, such as oil changes and tune-ups, due to their reliance on a single power source. The resale value of regular gasoline cars may decline faster than that of hybrid cars, especially as more buyers seek out fuel-efficient options.
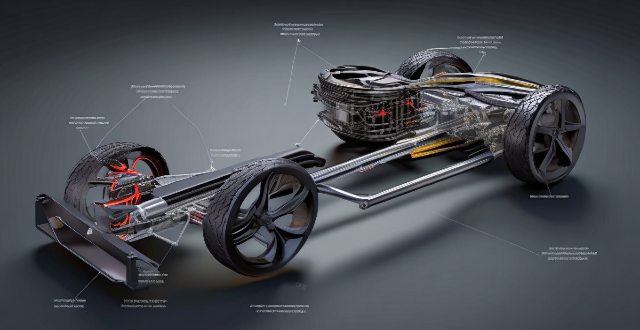
How does a gasoline hybrid car work ?
Gasoline hybrid vehicles, known as HEVs, merge an ICE with an electric motor for enhanced efficiency and reduced emissions. Key components include the ICE, electric motor, battery pack, transmission, and a generator/alternator. These cars can operate in various modes: fully on ICE power, purely electric, combined power, or through regenerative braking. The energy management controller optimizes power distribution for peak efficiency. Benefits of gasoline hybrids include better fuel economy, lower emissions, extended brake life, and potential tax incentives.

Are electric cars more expensive than gasoline cars ?
Electric cars, also known as EVs, have been gaining popularity due to their eco-friendly nature and lower operating costs. However, the initial purchase price of an electric car is often higher than that of a traditional gasoline-powered car. In this article, we will explore the cost differences between electric and gasoline cars. ## Upfront Cost **Electric Cars:** - Higher upfront cost due to expensive battery technology and limited production scale. - Prices vary depending on the model, brand, and range. - Some governments offer incentives and tax credits to offset the high initial cost. **Gasoline Cars:** - Generally less expensive upfront compared to electric cars. - Wide variety of models and brands available at different price points. - No government incentives or tax credits for purchasing a gasoline car. ## Operating Costs **Electric Cars:** - Lower operating costs due to cheaper electricity rates compared to gasoline prices. - Maintenance costs are generally lower since there are fewer moving parts in an electric motor. - Battery replacement can be costly, but it is not expected until after several years of use. **Gasoline Cars:** - Higher operating costs due to fluctuating gasoline prices and regular maintenance requirements. - More frequent oil changes, tune-ups, and other routine maintenance tasks. - Fuel efficiency varies widely among gasoline cars, affecting overall operating costs. ## Depreciation **Electric Cars:** - Depreciation rate may be higher for electric cars due to rapid advancements in technology and changing consumer preferences. - Some early adopters may experience significant depreciation if they choose to sell their electric car before its battery lifespan ends. **Gasoline Cars:** - Generally slower depreciation rate compared to electric cars. - Well-maintained gasoline cars can retain their value for longer periods. ## Resale Value **Electric Cars:** - Resale value depends on factors such as battery health, range, and charging infrastructure availability. - As more people switch to electric cars, the demand for used electric vehicles may increase, potentially boosting resale values. **Gasoline Cars:** - Resale value is typically more predictable and stable compared to electric cars. - Factors such as fuel efficiency, brand reputation, and vehicle condition affect resale value. In conclusion, while electric cars may have a higher upfront cost, they offer lower operating costs and potentially better resale value in the future. It's essential for consumers to consider both short-term and long-term costs when deciding between an electric or gasoline car.

Do gasoline hybrid cars require special maintenance ?
This text discusses the maintenance requirements for gasoline hybrid cars, which combine a conventional engine with an electric motor for added efficiency. While these vehicles do not require extensive special maintenance, there are specific components that need attention. Regular maintenance such as oil changes, tire rotations, brake checks, and air filter replacements are still essential. Additionally, hybrid-specific maintenance includes monitoring battery health, checking the regenerative braking system, ensuring proper cooling of the electric motor, and maintaining transmission fluid levels. It is important to refer to the vehicle's owner's manual for specific maintenance schedules and seek out professional service when needed. By addressing both conventional and hybrid-specific maintenance needs, gasoline hybrid cars can run reliably and efficiently.

What are the benefits of a gasoline hybrid engine ?
The article discusses the advantages of a gasoline hybrid engine, which is a combination of a traditional internal combustion engine and an electric motor. The benefits include improved fuel efficiency through reduced fuel consumption, regenerative braking, and start-stop technology; lower CO2 emissions and decreased pollutants resulting in cleaner air quality; and enhanced performance with instant torque, smooth driving experience, and extended brake life due to regenerative braking. Overall, gasoline hybrid engines provide a balance between power and efficiency, making them an attractive option for eco-conscious drivers.

What is the difference between a gasoline hybrid and an electric car ?
The main difference between a gasoline hybrid and an electric car is their fuel source and how they generate energy. Gasoline hybrids run on a combination of gasoline and electricity, while electric cars run solely on electricity. Gasoline hybrids produce lower emissions than traditional gasoline-powered vehicles but still require gasoline to operate. Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions but may still result in emissions from electricity production. Finally, gasoline hybrids typically have a longer range than electric cars due to their ability to switch between using gasoline and electricity depending on driving conditions.

How do parallel hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) compare to traditional gasoline cars in terms of performance ?
Parallel Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs) offer better acceleration and fuel efficiency than traditional gasoline cars but may have lower top speeds and require more time for recharging. Gasoline cars have higher top speed capabilities and quicker refueling but are less efficient and require more maintenance. The choice between the two depends on individual needs and preferences.

How far can a gasoline hybrid car travel on a full tank of gas ?
The text discusses the fuel efficiency and range of gasoline hybrid cars on a full tank of gas. Factors affecting fuel efficiency include driving habits, traffic conditions, vehicle maintenance, and weather conditions. Gasoline hybrid cars typically have higher fuel efficiency ratings than traditional gasoline-powered cars due to their combination of an electric motor and a gasoline engine. The estimated range of many gasoline hybrid cars is around 300-500 miles on a full tank of gas, with some having larger fuel tanks or higher fuel efficiency ratings allowing for greater ranges. Maximizing fuel efficiency can be achieved by considering factors such as driving habits and vehicle maintenance.

How do power batteries compare to traditional gasoline engines in terms of cost and efficiency ?
Power batteries and traditional gasoline engines are two different types of energy sources that are used to power vehicles. In this article, we will compare the cost and efficiency of power batteries and traditional gasoline engines. Power batteries have a higher initial cost than traditional gasoline engines, but require less maintenance and have lower fuel costs. They also have a higher energy conversion efficiency and can recharge through regenerative braking. However, they have a limited range compared to traditional gasoline engines. Traditional gasoline engines have a lower initial cost than power batteries, but require more maintenance and have higher fuel costs. They also have a lower energy conversion efficiency and cannot recharge through regenerative braking. However, they have a longer range than power batteries. Overall, while power batteries have a higher initial cost and limited range compared to traditional gasoline engines, they offer several advantages in terms of cost and efficiency. As technology continues to advance, it is likely that power batteries will become even more cost-effective and efficient compared to traditional gasoline engines.

How can governments implement policies to reduce plastic waste and pollution ?
Governments can implement policies to reduce plastic waste and pollution by banning single-use plastics, promoting recycling and composting programs, encouraging sustainable packaging practices, educating the public about plastic pollution, and collaborating with other countries and international organizations.

What are some innovative solutions for controlling plastic pollution in developing countries ?
The text discusses innovative solutions for controlling plastic pollution in developing countries, including promoting recycling and waste management, encouraging alternative packaging materials, educating the public on plastic pollution, implementing bans on single-use plastics, and investing in research and development.

How does plastic pollution impact marine life and ecosystems ?
The text discusses the impact of plastic pollution on marine life and ecosystems, including entanglement and ingestion by animals, chemical pollution from toxic additives, habitat destruction, food chain disruption, economic impacts on tourism and fishing industries, aesthetic and cultural impacts on coastlines and ocean environments, and solutions and mitigation efforts such as reducing plastic use, improving waste management, cleanup campaigns, education and awareness, policy changes, and research and innovation.

How do clean production technologies help reduce waste and pollution ?
Clean production technologies are vital in reducing waste and pollution. They achieve this through energy efficiency, resource efficiency, improved waste management, pollution control, and a holistic approach to sustainability via life cycle assessment. By implementing these technologies, industries can operate in a more sustainable manner, minimizing their environmental impact.

Is it more cost-effective to drive an electric or gasoline-powered car ?
In this article, we explored the cost-effectiveness of driving an electric car versus a gasoline-powered car. While electric cars may have a higher initial cost, they offer several advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness over the long term. Lower maintenance costs, cheaper fuel costs, and potential tax incentives make electric cars a more economical choice for many consumers. Additionally, electric cars have a smaller environmental impact compared to gasoline-powered cars, making them a more sustainable option for transportation.

How does air pollution caused by climate change affect children ?
The provided text discusses the impact of air pollution, exacerbated by climate change, on children's health. It outlines both immediate and long-term health effects, including respiratory issues, developmental concerns, chronic conditions, and potential for other health problems. The text also highlights the socio-economic impact of these health issues, such as school performance and healthcare costs. Prevention and mitigation strategies are suggested, including reducing pollution sources, promoting clean energy, awareness and education, and urban planning. The conclusion emphasizes the need for collective action to protect children's health and future.

What are the long-term effects of air pollution on our health ?
The long-term effects of air pollution on health are wide-ranging and severe, affecting individuals and entire communities. Respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, neurological disorders, reproductive health problems, and other health issues have all been linked to exposure to polluted air. It is essential to address air pollution as a public health issue to protect the health and well-being of people worldwide.

What are the most effective ways to control plastic pollution ?
The text discusses the issue of plastic pollution and its harmful effects on the environment and human health. It provides various methods to control this problem, including reducing plastic use, recycling properly, supporting eco-friendly brands, implementing government policies such as banning single-use plastics, promoting recycling infrastructure, and investing in research and development for sustainable alternatives to plastic. The text emphasizes that controlling plastic pollution requires collective efforts from individuals, businesses, and governments to achieve a cleaner and healthier environment for all living beings on Earth.

What is the role of businesses in controlling plastic pollution ?
Businesses have a crucial role in controlling plastic pollution. They can reduce plastic production by switching to biodegradable materials and improving recycling efficiency. Promoting sustainable practices, such as encouraging consumer responsibility and partnering with environmental organizations, is also essential. Investing in research and development for alternative products and improved recycling technologies further helps control plastic pollution. Businesses that prioritize sustainability will likely see long-term benefits in profitability and reputation.

What are the challenges faced by recycling facilities in controlling plastic pollution ?
Recycling facilities face numerous challenges in controlling plastic pollution, including logistical issues in collection and sorting, technological and economic constraints in processing, environmental concerns, and the need for public education. Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts from governments, industries, and individuals committed to reducing plastic pollution through effective recycling strategies.

How does proper waste management aid in saving energy and reducing pollution ?
Proper waste management is crucial for conserving energy and reducing pollution. It involves strategies like composting organic waste to reduce methane emissions, enhancing recycling to save energy in manufacturing new products, preventing environmental pollution through proper disposal, promoting sustainable practices like reduce, reuse, and recycle, and supporting the circular economy model. By adopting these measures, we can move towards a more sustainable future that conserves resources and protects our planet.

What impact does air pollution have on indoor sports facilities and athletes' health ?
Impact of Air Pollution on Indoor Sports Facilities and Athletes' Health: - **On Indoor Sports Facilities**: - Reduced visibility, unpleasant odors and tastes, equipment damage, and increased energy consumption due to air pollutants. - **On Athletes' Health**: - Respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, asthma attacks, skin irritation, fatigue and lethargy, cognitive impairment, and immune system suppression due to exposure to air pollutants.