Solar Heat

Can you explain the difference between photovoltaic and solar thermal energy ?
Solar energy harnesses the power of the sun to generate electricity or heat. Two major categories are photovoltaic (PV) and solar thermal systems, which differ in their conversion processes, applications, storage capabilities, efficiencies, and costs. PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials like silicon, while solar thermal systems capture the sun's heat to warm a fluid, usually water or air, which then provides heat or generates electricity. PV is mainly used for generating electricity, and solar thermal is used for both heating and electricity generation. Solar thermal systems can more readily incorporate thermal storage solutions, while PV systems typically require battery storage for off-grid applications. The cost and affordability depend on the specific application and location, with PV becoming increasingly competitive in recent years.

What are some examples of recent technological advancements in renewable energy sources ?
Renewable energy sources have been gaining momentum in recent years due to the increasing awareness of climate change and the need for sustainable alternatives to fossil fuels. Here are some examples of recent technological advancements in this field: - Solar Energy: Perovskite solar cells, bifacial solar panels, concentrated solar power (CSP) systems with efficient heat transfer fluids and storage systems. - Wind Energy: Floating wind turbines designed for deep waters, smart grid integration with improved forecasting techniques, demand response programs, and energy storage solutions. - Hydropower: Run-of-river systems that minimize environmental impact by utilizing natural river flow, low head hydropower installed in existing water infrastructure without significant modifications. - Geothermal Energy: Enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) with improved drilling techniques and efficient heat exchangers, low-temperature geothermal heat pumps harnessing warmth from Earth's surface even in colder climates. - Biomass Energy: Anaerobic digestion process breaking down organic matter to produce biogas for electricity generation or as a natural gas substitute, torrefaction converting biomass into coal-like substance called biocoal with higher energy density and potential applications in replacing coal in power plants and industrial processes.

How does solar energy work ?
Solar energy is generated through the use of solar panels containing photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity via the photovoltaic effect. This process involves absorbing sunlight, exciting electrons to a higher energy level, generating an electrical current, collecting it, and converting it into usable AC electricity. Solar energy is renewable, sustainable, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly, but its effectiveness can be reduced by weather conditions, and it requires additional equipment for energy storage. Despite high upfront costs, solar energy systems can lead to long-term savings on utility bills.
How do climate models account for factors such as ocean currents, atmospheric pressure, and solar radiation ?
Climate models are complex mathematical representations of the Earth's climate system, designed to simulate and understand the behavior of various components such as ocean currents, atmospheric pressure, and solar radiation. These factors play a crucial role in shaping our planet's climate, and their interactions are essential for accurate climate predictions. Ocean currents act as conveyor belts for heat, moving it from the equator towards the poles and helping to regulate global temperatures. Climate models use fluid dynamics equations to simulate the movement of water in the oceans, and observations from satellites and buoys are integrated into models to improve the accuracy of ocean current simulations. Atmospheric pressure influences weather patterns and is a key driver of wind systems around the globe. Numerical Weather Prediction (NWP) Models solve the Navier-Stokes equations to simulate atmospheric pressure changes over time, while Global Climate Models (GCMs) incorporate principles of thermodynamics and fluid dynamics to predict how pressure variations will impact climate. Solar radiation provides the primary energy source that drives Earth's climate system. Radiative Transfer Models (RTMs) calculate how solar radiation interacts with the atmosphere and Earth's surface, while Spectral Irradiance Models estimate the amount of solar energy reaching Earth based on sunspot activity and other solar cycles. Coupled Models combine RTMs with atmospheric and oceanic models to understand the full impact of solar radiation on climate.
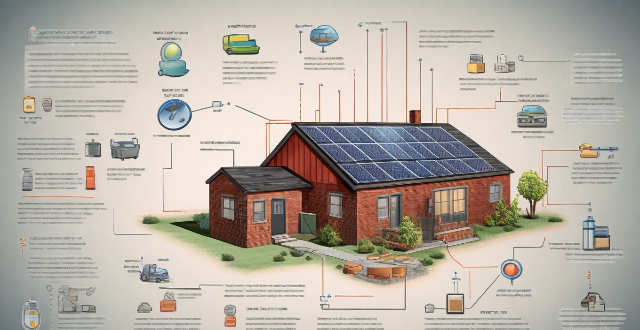
Is it possible to run my entire house on solar power alone ?
The possibility of powering an entire household with solar energy alone is influenced by various factors, including energy consumption habits, geographic location, available roof space, and system efficiency. Financial considerations, net metering policies, and maintenance requirements also play a role in determining the feasibility of such a setup. Homeowners should assess these elements and consider professional consultation to ascertain if their home can run solely on solar power.

What is the relationship between heat waves and mortality rates ?
The text discusses the relationship between heat waves and mortality rates, highlighting various factors that contribute to this complex relationship. It emphasizes the increased risk of heat-related illnesses like dehydration, heat exhaustion, and heat stroke during heat waves, which can lead to serious complications and death if not treated properly. The article also notes the impact of heat waves on chronic health conditions like cardiovascular disease, respiratory problems, and diabetes. Age-related vulnerabilities are discussed, with older adults being particularly susceptible due to physiological changes and a higher prevalence of chronic health conditions. Socioeconomic factors are identified as crucial determinants of an individual's vulnerability to the adverse effects of heat waves, including housing quality, healthcare access, education level, and employment status. The text concludes by stressing the importance of public health strategies aimed at reducing the impact of heat waves on vulnerable populations.

How do solar panels impact electricity bills in the long run ?
Solar panels can significantly reduce electricity bills over the long term by reducing energy consumption, increasing self-sufficiency, and taking advantage of net metering programs. While the initial cost of installation can be high, lower operating costs, federal tax credits, and increased home value can help offset these expenses. Additionally, solar panels offer environmental benefits such as reduced carbon emissions and support for renewable energy infrastructure.

Are there any government incentives for installing solar panels ?
Governments worldwide offer various incentives to encourage the adoption of solar energy, including tax credits and deductions, rebates, net metering, feed-in tariffs, grants, low-interest loans, green energy certificates, and solar rights laws. These incentives aim to reduce the upfront costs of installing solar panels and make renewable energy more accessible and financially viable for homeowners and businesses. However, eligibility requirements and application processes can vary, so it's essential to consult local professionals or agencies for specific information.

How long do solar panels typically last ?
Solar panels are a sustainable and cost-effective way to generate electricity. However, the lifespan of solar panels is an important factor to consider when making an investment in renewable energy. In this article, we will explore how long solar panels typically last and what factors can affect their lifespan. Solar panels are designed to last for several decades, with most manufacturers offering warranties of 25 years or more. However, the actual lifespan of a solar panel can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of materials used, the installation process, and environmental factors. The quality of the materials used in the manufacturing process can significantly impact the lifespan of a solar panel. Proper installation ensures that the panel is securely mounted and protected from potential damage caused by weather conditions or other external factors. Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and exposure to sunlight can also impact the lifespan of a solar panel. To ensure that your solar panels last as long as possible, it is essential to perform regular maintenance checks. This includes keeping the panels clean, checking for damage, and monitoring performance over time. By following proper maintenance practices and monitoring your solar panel's performance over time, you can ensure that your investment in renewable energy pays off in the long run.

How do urban greening projects influence city temperatures and heat islands ?
Urban greening projects, such as planting trees and creating parks, can help reduce city temperatures and mitigate the effects of urban heat islands. These projects provide shade, reduce heat absorption by buildings and roads, and promote evapotranspiration, all of which contribute to cooler city environments. By increasing vegetation in cities, urban greening initiatives can also help reduce the intensity of urban heat islands, making cities more comfortable for residents. As our world continues to urbanize, prioritizing urban greening initiatives is essential for creating healthier and more sustainable cities for future generations.

What are the benefits of using solar power ?
Solar power is a renewable and sustainable energy source that offers numerous benefits. It can be cost-effective in the long run, environmentally friendly, promotes energy independence, has low maintenance costs, versatile applications, creates jobs, provides government incentives, increases property value, and enhances energy security. As technology advances and awareness grows about renewable energy sources like solar power, its adoption is expected to continue rising worldwide.

How does wind energy compare to solar energy ?
Wind energy and solar energy are both renewable sources of energy that have gained popularity in recent years. Wind turbines can generate electricity with high efficiency and low maintenance cost, while solar panels have a low initial cost and long lifespan. However, wind turbines can create noise pollution and have limited availability, while solar panels rely on sunlight and require a large amount of land. Both sources have their advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications.

How can I identify and respond to signs of heat exhaustion or heatstroke ?
Heat exhaustion and heatstroke are two serious conditions that can occur when the body overheats, often due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and dehydration. Recognizing the symptoms of each is crucial for timely treatment. Heat exhaustion symptoms include heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, muscle cramps, pale skin, headache, confusion, and rapid heartbeat. Heatstroke signs involve fever, altered mental state, hot dry skin, rapid breathing, racing heart rate, nausea and vomiting, severe headache, and possibly seizures. Immediate action is required: for heat exhaustion, move to a cooler area, hydrate, cool down, and rest; for heatstroke, call emergency services, move to shade, lower body temperature, lighten clothing, stay hydrated, and monitor vital signs. Prevention involves avoiding strenuous activities during peak heat, wearing appropriate clothing, staying hydrated, and recognizing personal limits.

How much does it cost to install a solar panel system ?
The cost of installing a solar panel system varies depending on the size, type of panels used, and installation location. Small residential systems typically range from $15,000 to $25,000 before tax credits or incentives, while medium to large residential systems can cost between $25,000 to $40,000. Commercial systems can vary greatly in size and cost. Monocrystalline silicon panels are the most efficient and expensive option, while thin-film solar panels are the least expensive but also less efficient. Rooftop installations are generally more expensive than ground-mounted installations. Additional costs include inverters, batteries, and installation fees. It is important to consult with a reputable solar installer for an accurate estimate based on specific needs and circumstances.

How can I maintain and clean my solar panels for optimal performance ?
The article discusses the importance of maintaining and cleaning solar panels to ensure their optimal performance. It provides a detailed guide on how to keep solar panels in top condition through regular inspection, cleaning, preventative measures, and safety precautions. The guide includes steps for visual inspection, checking for shading, monitoring production levels, dry and wet cleaning methods, using bird repellents and gutter guards, and routine maintenance. It also emphasizes the importance of wearing appropriate safety gear and taking precautions when working on or around solar panels. By following these steps, homeowners can extend the lifespan of their solar panels and maintain their efficiency over time.

How does solar power work and is it a viable option for homes ?
Solar power is generated through solar panels made of silicon cells that convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity. This process involves absorption of light, conversion to DC, conversion to alternating current (AC), and distribution throughout a home or business. Solar power is a viable option for homes due to its renewable nature, cost savings, environmental benefits, and government incentives. However, weather conditions, storage options, and upfront costs should also be considered before deciding if solar power is the right choice for your home.

What are the advantages of using solar panels for residential and commercial purposes ?
Solar panels offer reduced energy costs, environmental benefits, increased property value, energy independence, low maintenance, and government incentives for residential and commercial use.

How does solar power generation work and is it a viable option for residential use ?
Solar power generation involves converting sunlight into electricity using solar panels, which are made up of photovoltaic cells. The process includes generating electricity, converting it from DC to AC, net metering, and battery storage. Solar power is a viable option for residential use due to its cost-effectiveness, energy independence, environmental benefits, increased property value, and technological advancements.

What is the role of renewable energy sources in energy-efficient buildings ?
Renewable energy sources play a crucial role in the construction and operation of energy-efficient buildings, providing clean, sustainable power that reduces reliance on fossil fuels and helps mitigate climate change. Solar energy is one of the most popular renewable energy sources used in energy-efficient buildings, harnessing the power of the sun to generate electricity or heat water for use in buildings. Wind energy converts the kinetic energy of wind into electricity, which can then be used to power buildings. Geothermal energy involves harnessing the heat from the earth's core to provide heating and cooling for buildings. Biomass energy uses organic materials such as wood chips, crop waste, and animal manure to generate heat and electricity for buildings. Hydropower involves using the energy of moving water to generate electricity. Incorporating these technologies into building designs and operations can create more sustainable and environmentally friendly structures that benefit both people and the planet.

What are the alternatives to fossil fuels for energy production ?
The article discusses various alternatives to fossil fuels for energy production, including solar energy, wind energy, hydroelectric power, geothermal energy, biomass energy, and nuclear energy. It explains the working principles of each alternative and their advantages and disadvantages. The main advantage of these alternatives is that they produce clean energy with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, reducing the impact on the environment and climate change. However, some of them require significant investment and infrastructure development, while others have safety concerns or limited availability. Overall, the article highlights the potential of these alternatives in providing sustainable and reliable sources of energy for the future.

What are some innovative ways that people are using to generate their own alternative energy at home ?
The provided text discusses innovative ways to generate alternative energy at home. It mentions various methods such as solar power (solar panels, solar water heaters, solar chargers), wind power (home wind turbines, vertical axis wind turbines), hydropower (micro hydro systems, rainwater harvesting), geothermal energy (ground source heat pumps, geothermal water heaters), and biomass energy (wood burning stoves, biogas digesters). The conclusion highlights the potential of these methods in reducing a household's carbon footprint and contributing to a sustainable future.

What are the most common types of renewable energy sources ?
Renewable energy sources are naturally replenished and provide a sustainable way to generate power without depleting the Earth's natural resources or contributing to climate change. Solar energy is harnessed through photovoltaic systems, solar water heaters, and concentrating solar power. Wind energy is captured by onshore and offshore wind turbines. Hydropower is generated through dam-based and run-of-river systems. Geothermal energy is tapped into via dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle power plants. Bioenergy includes biomass combustion, anaerobic digestion, and biofuels. These sources offer clean alternatives to fossil fuels and play a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

What are the most promising renewable energy technologies for reducing carbon emissions ?
Renewable energy technologies are crucial for reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. They harness natural resources such as wind, solar, hydro, geothermal, and biomass to produce electricity or heat without emitting greenhouse gases. This article discusses the most promising renewable energy technologies for reducing carbon emissions. Solar energy can be generated through photovoltaics (PV) or concentrated solar power (CSP). Wind energy is growing rapidly due to its low cost and minimal environmental impact. Hydropower is a significant source of clean power but has environmental concerns. Geothermal energy has a high capacity factor but limited availability. Bioenergy helps reduce dependence on fossil fuels but requires careful consideration of land use changes. Wave and tidal energy have immense potential but are still in early development stages. Overall, these technologies offer unique benefits and challenges for creating a sustainable future.

What is the current state of renewable energy research and development ?
Renewable energy research and development (R&D) is a rapidly evolving field that aims to create sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. The current state of renewable energy R&D can be characterized by several key trends: ### **Advances in Technology** - Solar energy research focuses on improving the efficiency of photovoltaic cells and concentrated solar power systems. - Wind energy technology is advancing with the development of offshore wind turbines and material innovations for turbine blades. - Hydropower research explores ways to harness energy from small streams and rivers without ecological harm, as well as improvements to pumped storage systems. - Geothermal energy is expanding beyond natural hotspots through enhanced geothermal systems and binary cycle power plants. ### **Integration with Grid Systems** - Smart grids enable better management of consumer demand and integrate distributed energy resources like rooftop solar panels and small wind turbines. - Energy storage solutions, such as battery technologies and pumped hydro storage, are being refined for improved efficiency and environmental impact. ### **Policy and Economic Drivers** - Government incentives like tax credits and feed-in tariffs encourage renewable energy adoption. - Carbon pricing mechanisms, including emissions trading schemes and carbon taxes, create financial incentives for companies to reduce their greenhouse gas emissions. ### **Environmental Impact and Sustainability** - Lifecycle analysis examines the manufacturing processes and end-of-life management of renewable energy equipment to minimize environmental footprint. - Biodiversity conservation efforts aim to mitigate the impact of renewable energy infrastructure on wildlife habitats and ecosystems. As technological innovation, grid integration advancements, supportive policies, and consideration for environmental impact continue, renewable energy is expected to play an increasingly vital role in global energy supply while helping to mitigate climate change.

What are the causes of the greenhouse effect ?
In this article, we explore the natural and human-intensified causes of the greenhouse effect and its potential consequences. The greenhouse effect is a process where certain atmospheric gases trap heat from the sun, warming the Earth's surface. Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and agricultural practices have increased the levels of these gases, leading to an intensified greenhouse effect and contributing to global warming. The consequences of an intensified greenhouse effect include rising temperatures, melting ice caps and glaciers, extreme weather events, ecosystem disruption, and impacts on human health. To address these challenges, collective action is needed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and transition to sustainable practices.

Can you provide examples of successful resource-efficient utilization projects ?
The text discusses several successful resource-efficient utilization projects, including waste-to-energy, solar power, water conservation and recycling, sustainable agriculture, and energy efficiency improvements in buildings. Each project aims to reduce waste, conserve resources, and generate renewable energy. Examples include Singapore's NEWater Plant, CopenHill Waste-to-Energy Plant in Copenhagen, Topaz Solar Farm in California, Tesla's Solar Roof Tiles, Singapore's New Aquarium, Orange County Water District's Groundwater Replenishment System, The Market Garden in Vermont, Fairtrade Coffee Cooperatives, Empire State Building Renovation, and Passive House Design.